Parallel Implementation
In this stage, you are required to write code to evolve Game of Life using multithreading on a single machine.
The following pages are some suggested steps to help you get started, you are not required to follow them.
Your implementation will be marked against the success criteria outlined here.
Step 1
Implement the Game of Life logic as it was described in the task introduction.
We suggest starting with a single-threaded implementation that will serve as a starting point in subsequent steps.
Your Game of Life should evolve for the number of turns specified in struct Params.
Your Game of Life should evolve the correct image specified by image_width and image_height.
// Params struct is defined in `src/gol/mod.rs`
pub struct Params {
pub turns: usize,
pub threads: usize,
pub image_width: usize,
pub image_height: usize,
}The skeleton code starts two async tasks (coroutines). The diagram below shows how they should interact with each other.
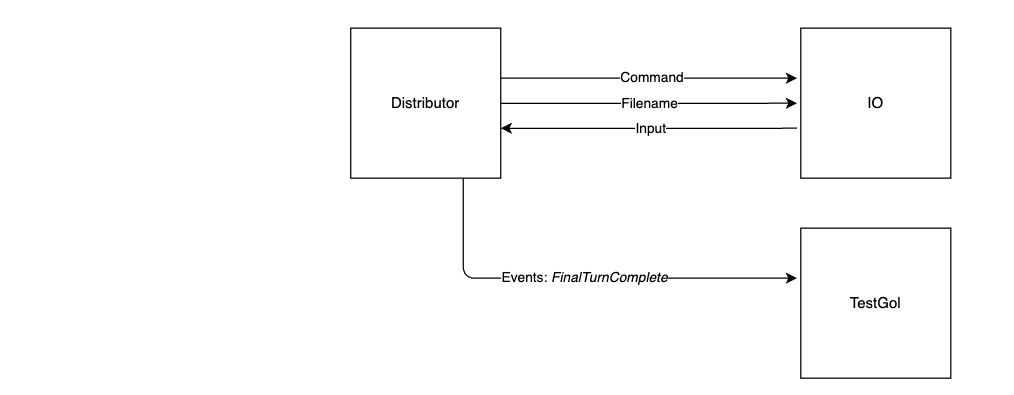
Note that not all channels linking IO and the Distributor have been initialised for you.
You will need to create them and add them to the io_channels and distributor_channels structs.
These structs are created in src/gol/mod.rs.
// in `src/gol/mod.rs`
let io_channels = IoChannels {
command: Some(io_command_rx),
idle: Some(io_idle_tx),
filename: None, // Create me first
output: None, // Create me first
input: None, // Create me first
};
let distributor_channels = DistributorChannels {
events: Some(events),
key_presses: Some(key_presses),
io_command: Some(io_command_tx),
io_idle: Some(io_idle_rx),
io_filename: None, // Create me first
io_output: None, // Create me first
io_input: None, // Create me first
};Then move on to src/gol/distributor.rs, this will be the main entrance you start writing your Gol implementation.
IO
You are not able to call methods directly on the IO coroutine. To use the IO, you will need to utilise channel communication.
To read the initial PGM image, you will need the command, filename and input channels. Look at the file src/gol/io.rs for their implementation details.
The functions read_pgm_image and start_io are particularly important in this step.
Events
Your Game of Life code will interact with the user or the unit tests using the events channel. All events are defined in the file src/gol/event.rs. In this step, you will only be working with the unit test gol_test.rs. Therefore, you only need to send the FinalTurnComplete event.
MPMC channels
In the skeleton, the flume channel is widely used.
Flume is a multi-producer, multi-consumer (MPMC) channel that functions similarly to a Golang channel.
Tips on improving the performance - counting neighbours
We have provided you with a basic solution that uses modulo operations (%) to calculate the coordinates of neighbours, but it can still be further optimised because modulo usually takes more CPU cycles - they are slow.
It is recommended to back up your various implementations; this will be helpful for analysing how well you did in the later stages.
Test
To test your serial, single-threaded implementation, type the following in the terminal, all the tests ran should pass.
cargo test --release --test gol -- --threads 1