Parallel Implementation
In this stage, you are required to write code to evolve Game of Life using multiple worker goroutines on a single machine.
The following pages are some suggested steps to help you get started, you are not required to follow them.
Your implementation will be marked against the success criteria outlined here.
Step 3
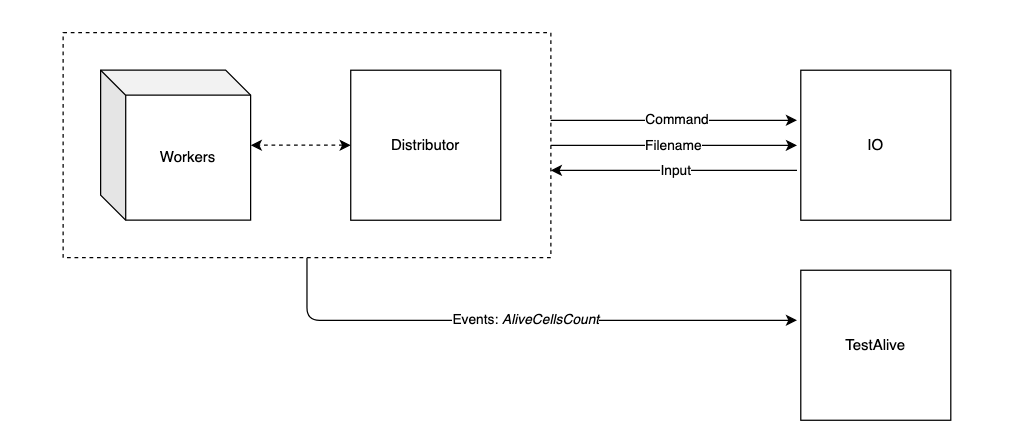
The lab sheets included the use of a timer.
Now using a ticker, report the number of cells that are still alive every 2 seconds.
To report the count use the AliveCellsCount event.
Run your implementation
When running your implementation, you will get the average Game of Life iteration turns per second (Avg turns/s).
You can use this data to evaluate your performance and compare it with your various implementations. However, we do not recommend directly using this data in your report. We recommend using formal benchmarking instead, and don't forget to analyse your methods and results in your report.
To run your implementation, type the following in the terminal.
To stop the program, press CTRL+C twice in the terminal.
go run . -headless -t 4The
-headlessargument disables the SDL visualiser for this run, as we haven't implemented it yet.The
-targument stands for the number of threads passed togol.Params.Threadsfor this run; you can specify this number yourself.
Test
To test your implementation, type the following in the terminal.
go test ./tests -v -run TestAliveTroubleshooting
You can check what the correct number of alive cells is by looking at the .csv files in the check/alive/ folder.
You might find that you are reporting the count for the turn before or turn after. If this happens the CompletedTurns might be what is wrong, not the count