Extensions
Below are suggested extensions. They vary in difficulty.
There are many other possible extensions to Game of Life. If you'd like to implement something that isn't an option below you're welcome to do so, but please speak to a lecturer first.
Halo Exchange
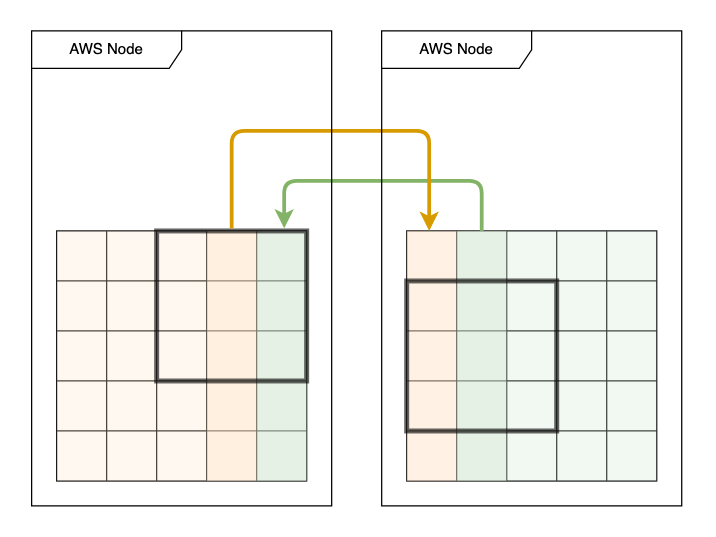
Recall that to process an iteration of Game of Life, each worker needs two extra rows (or columns). These are known as the halo regions. They need to be updated with data from neighbouring workers to process each iteration correctly.
The easiest solution is to have all workers resync with a central distributor node on every iteration. This introduces a heavy communication overhead (which you might be able to measure).
Implement a Halo Exchange scheme, where workers communicate the halo regions directly to each other. Analyse the performance of your new solution and compare it with your previous implementation.
Parallel Distributed System
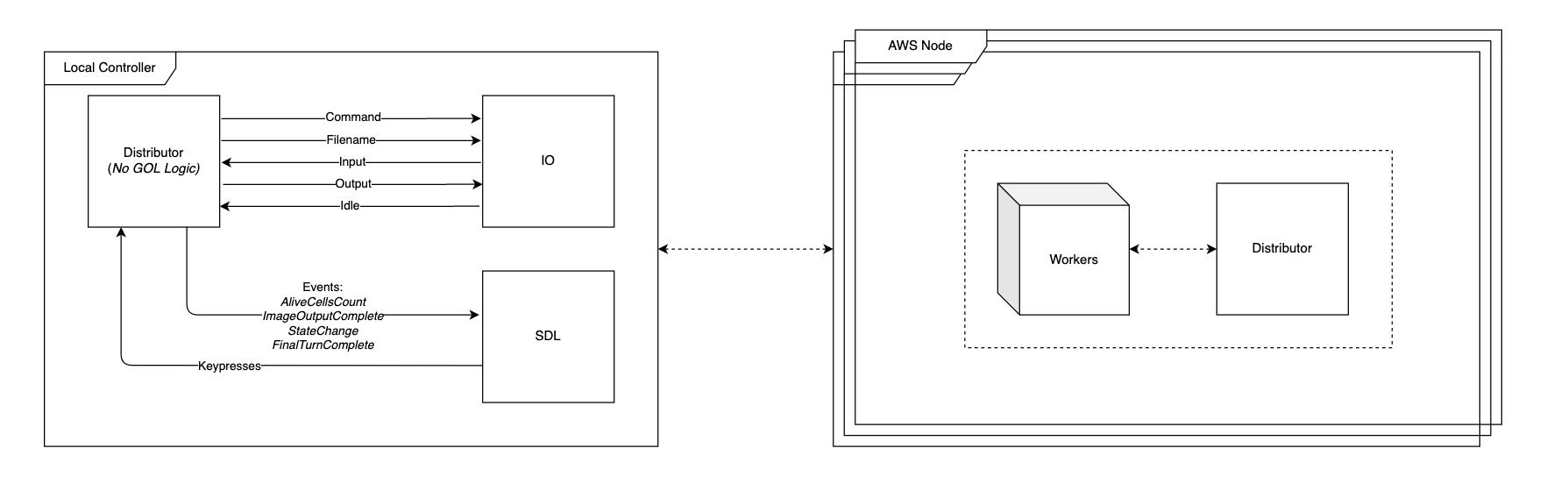
Add parallel workers within each distributed AWS Node.
Analyse the performance of your new solution and compare it with your previous implementation. Use various provided PGM images and analyse the effect on performance in context of the image size.
SDL Live View of Distributed Implementation
Instead of showing a blank SDL window in your local controller, add support for a Live View, in a similar way to the parallel implementation. Try to keep your implementation as efficient as possible.
Analyse the performance of your new solution and compare it with your previous implementation. Quantify and explain the overhead (if any) added by the Live View.
Fault Tolerance
Add fault tolerance to your Distributed Implementation.
In your report, explain the design of your fault tolerance mechanism. Conduct experiments to verify the effectiveness of your fault tolerance approach.
Memory Sharing
Redesign your parallel implementation to use pure memory sharing. Replace all channels with traditional synchronisation mechanisms (mutexes, sempahores, condition variables).
We recommend first replacing any channels used between the workers and the distributor.
Then remove channels linking the distributor with the IO and with SDL.
You should still keep them as seperate goroutines. Your solution must be free of deadlocks and race conditions.
Analyse the performance of your new solution and compare it with your previous implementation. Explain any differences observed.